New Insights for 2025: How States Are Funding and Expanding Short-Term Credential Pathways
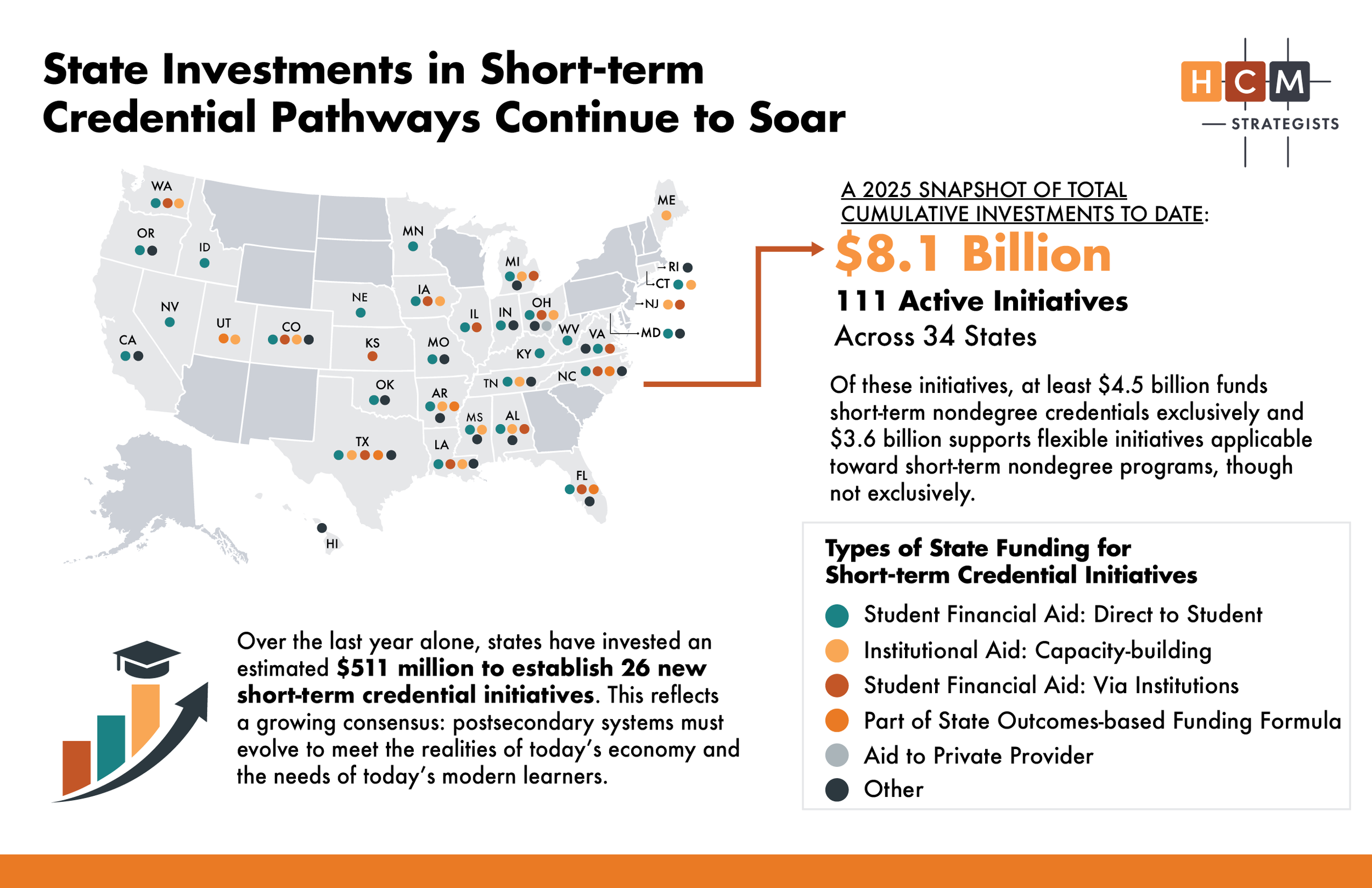
Today, we release the 2025 update to our typology and landscape analysis of state investments in short-term credential pathways. HCM’s latest and most comprehensive analysis identifies 111 active state-funded initiatives across 34 states.
Of the 111 active initiatives, 69 exclusively fund short-term nondegree credentials or short-term, skills-based workforce training programs. These represent a total investment of at least $4.5 billion to date. An additional $3.6 billion supports initiatives that can be applied to short-term nondegree programs, though not exclusively. Combined, these active investments amount to at least $8.1 billion in state funding.
Key Insights
Over the past year alone, states have committed approximately $511 million to launch 26 new short-term credential initiatives, a clear sign that states continue to significantly expand their investments in short-term, nondegree credentials at a moment of rapid change in national workforce and higher education policy. With the passage of the Workforce Pell Grant in 2025, the federal government has created the most substantial expansion of student aid in decades, opening need-based funding to high-quality, workforce-aligned programs as short as eight weeks. At the same time, artificial intelligence and shifting labor-market demands are accelerating the need for faster, more flexible learning pathways that help learners upskill throughout their careers. Together, these forces are reshaping how states design and govern credential programs—and creating a critical opportunity to build systems that expand economic mobility and strengthen the workforce.
States continue to invest in short-term, nondegree credentials as national policy reforms and shifting workforce needs reshape the training ecosystem.
The 2025 passage of the Workforce Pell Grant marks a historic expansion of federal student aid, extending need-based funding to short, workforce-aligned programs beginning in 2026.
Programs seeking Pell eligibility must meet rigorous quality and labor-market standards, including accreditation, employer validation, stackability, strong completion and placement outcomes, and evidence of positive earnings gains.
If effectively implemented, Workforce Pell could transform how the U.S. prepares its workforce, enabling faster pathways into high-demand fields and positioning community colleges as key engines of regional economic mobility.
AI and automation are rapidly reshaping job requirements, shortening the lifespan of technical skills and heightening the need for continuous reskilling through modular, flexible credential pathways.
These changes signal a shift toward a more accountable, learner-centered, and data-driven credentialing system, with employers and accreditors playing increasing roles in validating program quality.
States face a pivotal moment to build the policies, governance structures, and partnerships needed to translate federal momentum into equitable opportunity, stronger labor markets, and sustained economic growth.
Read the full report to learn more: A 2025 Update on Short-term Credential Pathways
Acknowledgements: We thank Lumina Foundation for its generous support of this project. Lumina’s continued commitment to expanding educational opportunity and strengthening the nation’s credentialing landscape made this research possible. We also extend our appreciation to the state partners and intermediary organizations participating in Lumina’s FutureReady States initiative for contributing essential data that enriched and completed our analysis. This publication updates A Typology and Policy Landscape Analysis of State Investments in Short-term Credential Pathways, first released in 2023 and updated in 2024.